- Home
- Knowledge library
- The UK aphid monitoring network
The UK aphid monitoring network
Find out about the national network of aphid suction traps and yellow water traps. Delivering regional information on aphid species and numbers (and BYDV), these monitoring resources can guide insecticide treatment decisions.
The suction-trap network
The suction-trap network focuses on aphid species of importance to cereals and oilseeds crops. It is managed by Rothamsted Insect Survey (RIS) and funded by the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BBSRC).
The 12.2m tall traps suck in air continuously and are emptied daily during the ‘aphid season’. Each trap represents aphid-flight activity over a radius of around 80 km. Aphid species are then identified and counted at Rothamsted Research and SASA (Gogarbank suction trap).
Aphid counts are presented across a ‘bulletin week’ (which runs from Monday to Sunday).
In 2020, RIS introduced a free text messaging service to inform cereal growers about the number of aphid vectors in their area. In 2021, this service replaced the PDF/email service called Aphid News.
BYDV monitoring (background)
We provide a regular snapshot of the proportion of virus-carrying cereal aphids (bird cherry-oat and grain aphids).
Mainly issued during the autumn, the results are based on (BYDV/CYDV) tests of a small number of aphid samples collected from four suction traps (see map). The work screens up to 96 aphid samples each week.
Virus monitoring has been conducted at the same sites since 2019 (originally as part of a BYDV management research project).
The longer-term resource is building a picture of how virus levels fluctuate on a seasonal and regional basis.
Results show that most aphids do not carry BYDV. For example, average results from autumns 2021, 2022, 2023 and 2024 showed that the proportion of viruliferous aphids did not exceed 30% (although, some weekly results did exceed this figure).
The results also show over-season trends. For example, virus levels tend to be highest at sites in regions with more permanent grassland (which acts as a reservoir for aphids and BYDV).
An AHDB research project that concluded in 2023 found that suction trap data on the percentage of aphids carrying the virus was reliable over a greater area than previously thought, with accuracy good up to 40 km away.
BYDV variants/isolates
BYDV is a complex of viruses made up of variants/isolates, with some transmitted by more than one aphid species. For example:
Luteovirus (genus)
- BYDV-PAV is spread by several aphids, including bird cherry-oat aphids and grain aphids
- BYDV-MAV is spread by grain aphids
Polerovirus (genus)
- CYDV-RPV (formerly BYDV-RPV) is mainly spread by bird cherry-oat aphids
Notes: A genus contains closely related species. The two genera cited are distinct and related (but not as closely related as the viruses within each genus).
CYDV = Cereal yellow dwarf virus.
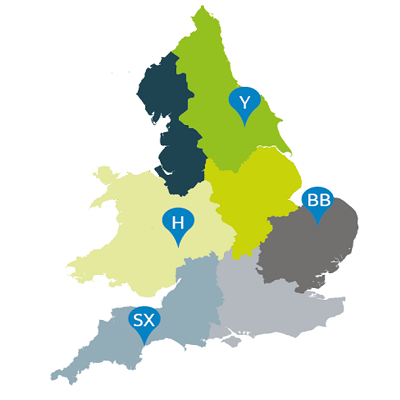
BYDV monitoring locations
 AHDB
AHDB
- York (Y)
- Hereford (H)
- Broom’s Barn (BB)
- Starcross (SX)
BYDV monitoring (results)
Autumn 2025 results
28 November 2025
The latest data corresponds to the Rothamsted Research Insect Survey 2025 bulletin 34 (17 November to 23 November 2025).
16 aphids were tested:
- 16 bird cherry-oat aphids (2 positive)
- 0 grain aphids (0 positive)
Note: Aphid numbers have declined across the UK.
Latest data (bulletin week)
|
Bird cherry-oat aphid (latest weekly data) |
|||||
|
Suction trap |
Total tested |
BYDV (PAV + MAV) |
CYDV (RPV) |
Total with virus |
Proportion with virus (%) |
|
York (Y) |
0 |
0 | 0 | 0 | N/A |
|
Hereford (H) |
1 |
0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
|
Broom’s Barn (BB) |
2 |
1 | 0 | 1 | 50 |
|
Starcross (SX) |
13 |
1 | 0 | 1 | 8 |
|
Grain aphid (latest week) |
|||||
|
Suction trap |
Total tested |
BYDV (PAV + MAV) |
CYDV (RPV) |
Total with virus |
Proportion with virus (%) |
|
York (Y) |
0 |
0 | 0 | 0 | N/A |
|
Hereford (H) |
0 |
0 | 0 | 0 | N/A |
|
Broom’s Barn (BB) |
0 |
0 | 0 | 0 | N/A |
|
Starcross (SX) |
0 |
0 | 0 | 0 | N/A |
Cumulative data (all bulletin weeks)
|
Bird cherry-oat aphid (cumulative) |
|||||
|
Suction trap |
Total tested |
BYDV (PAV + MAV) |
CYDV (RPV) |
Total with virus |
Proportion with virus (%) |
|
York (Y) |
396 |
93 | 57 | 150 | 38 |
|
Hereford (H) |
312 | 76 | 48 | 124 | 40 |
|
Broom’s Barn (BB) |
253 |
45 | 15 | 60 | 24 |
|
Starcross (SX) |
267 |
60 | 29 | 89 | 33 |
|
Grain aphid (cumulative) |
|||||
|
Suction trap |
Total tested |
BYDV (PAV + MAV) |
CYDV (RPV) |
Total with virus |
Proportion with virus (%) |
|
York (Y) |
17 |
3 | 0 | 3 | 18 |
|
Hereford (H) |
7 |
3 | 0 | 3 | 43 |
|
Broom’s Barn (BB) |
9 |
2 | 0 | 2 | 22 |
|
Starcross (SX) |
12 |
5 | 0 | 5 | 42 |
|
All aphids (cumulative) |
|||||
|
Suction trap |
Total tested |
BYDV (PAV + MAV) |
CYDV (RPV) |
Total with virus |
Proportion with virus (%) |
|
York (Y) |
413 |
96 | 57 | 153 | 37 |
|
Hereford (H) |
319 |
79 | 48 | 127 | 40 |
|
Broom’s Barn (BB) |
262 |
47 | 15 | 62 | 24 |
|
Starcross (SX) |
279 |
65 | 29 | 94 | 34 |
|
Totals |
1,273 |
287 | 149 | 436 | 33.6 |
A note on accumulated data
Accumulated data may include results from back-tests on aphids caught in earlier bulletin weeks. As a result, the accumulated data may be higher than expected (based on the latest weekly data).
BYDV management tool
Time your cereal insecticide sprays for aphid/BYDV control with greater accuracy.
March aphid forecasts
Suction trap aphid data and weather data can be used to forecast the start of aphid flights. Although there is considerable uncertainty associated with actual first flight dates at specific sites, the forecasts provide an indication of how early or late flights will take place, compared with an ‘average’ season. It is important to note that some aphids overwinter in crops and are likely to be present before aphid flights commence.
The yellow-water-trap network
Fera manages a network of yellow water traps. Compared to the suction trap network, these traps provide more localised (and more recent) information on which aphids are flying close to seed potato crops. Funding from AHDB Potatoes supported this service until statutory levy collection for this sector ceased (2004–21).
Further information
How to recognise and manage aphids in cereals and oilseed rape
Insecticide Resistance Action Group (includes aphid sampling protocol)
Management of aphid and BYDV risk in winter cereals (research project)
Further information on BYDV management and research (2021 video)
What is the value of BYDV tolerance/resistance in cereals? (2021 video)

