- Home
- Knowledge library
- Distribution and biology of winter wild-oat in the UK
Distribution and biology of winter wild-oat in the UK
Winter wild-oat is competitive in arable crops and can cause yield losses in cereals. Find out how to identify and control it.
Overview
Wild-oat (Avena sterilis) reproduces only by seed; it germinates in autumn and persists over winter. One wild-oat plant per square meter can reduce yields by up to 1t/ha in winter cereals and up to 0.6t/ha in spring cereals.
- It is particularly competitive in winter wheat, winter oilseed rape and spring crops
Description
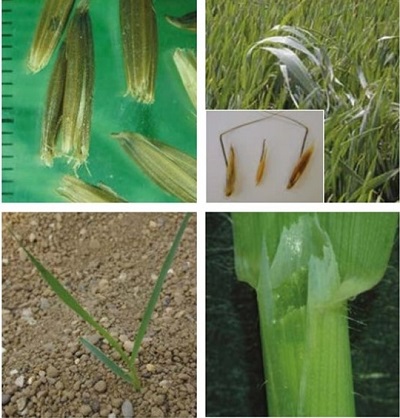
It is a tall, stout, annual grass similar to cultivated oat. The leaf blade is broad and flat with an anticlockwise twist. The flowerhead is spreading with drooping spikelets.
Key features
Fruit: Winter wild-oat has a narrower lemma than that of wild-oat and a shorter awn. The seeds are joined in the spikelet and require pressure to prize apart, leaving a scar.
Lookalikes
All the oat species are difficult to tell apart – at the seedling and adult stages.
Winter wild-oat germinates in the autumn, while wild-oat usually germinates in the spring.
Compared with winter wild-oat, the leaf margins of wild-oat are hairier near the base and the spikelets are smaller, lemmas are broader and end in two small teeth. The two species are easier to tell apart when the fruit is ripe, wild-oat seeds separate from the spikelet with no scar.
The ligule of cultivated oat is shorter and blunter than that of wild-oat. The leaves are hairless. When mature, cultivated oat is generally broader-leaved, paler and more robust than wild-oat species.

Location and life cycle
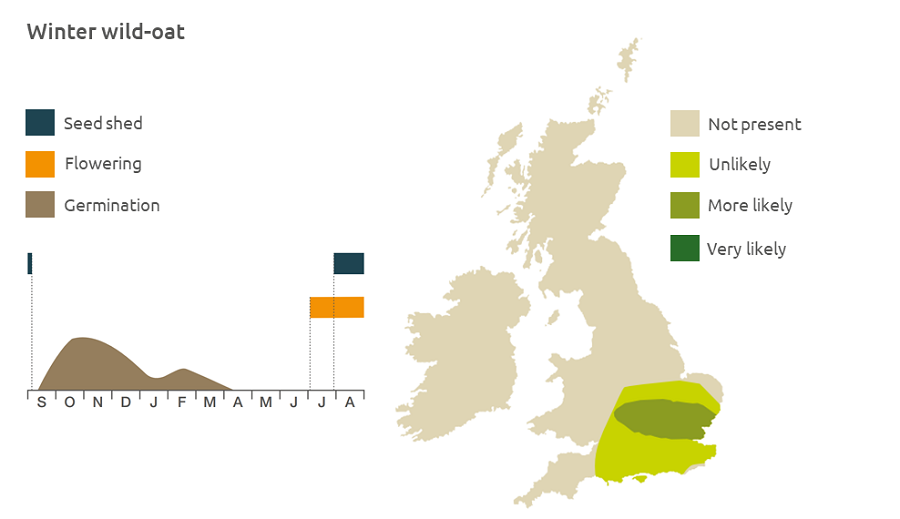
Geographic distribution
The range of winter wild-oat has grown from its focus in Oxfordshire into East Anglia and the Midlands. It is a lowland plant found on waste ground.
Soil type
It grows on heavy clay soils.
Seed statistics
- Seed longevity: 1–5 years
- Seed weight: 66.67 mg
Management
Control is cheaper in break crops; use of stale seedbed in autumn or spring will help. Delay cultivation after harvest to allow seed predation. Hand roguing is possible when plants are visible above the crop. Clean the combine between fields to prevent seeds being spread.
For advice on herbicides, please speak with your agronomist or adviser.
Herbicide resistance
Herbicide resistance in wild oat has been detected on over 250 farms and 28 counties, mainly across England*. Although less problematic than black-grass, the situation requires careful management. Resistance is also present in winter wild oats, although resistance in this species has not been extensively studied.
*Based on a compilation of data in 2016 from most organisations/companies testing for herbicide resistance in the UK.
When was this information last updated?
This page is based on content from the encyclopaedia of arable weeds publication. Since it was first released in 2008, the publication has been redesigned several times but not revised. However, it remains a good foundation for general information on the distribution and biology of weeds.

