- Home
- Knowledge library
- Distribution and biology of wild radish in the UK
Distribution and biology of wild radish in the UK
Wild radish is a very common weed that is difficult to control in brassica crops. Find out how to identify and control it.
Overview
Wild radish (Raphanus raphanistrum), also called runch, is one of the commonest weeds worldwide. It emerges mostly in spring and therefore in spring crops, but it germinates also in early-sown winter oilseed rape. These autumn-germinating seedlings are generally killed by frosts but can persist in a mild winter. The seed can be transported as a seed contaminant and can remain viable in manures. Statutory seed regulations for the UK and for England (2002) specify that the seeds must not be found in cereal grain samples. It is a particular problem in oilseed rape crops where the seed cannot be separated.
- It is particularly competitive in winter oilseed rape
- It has value to biodiversity
Description
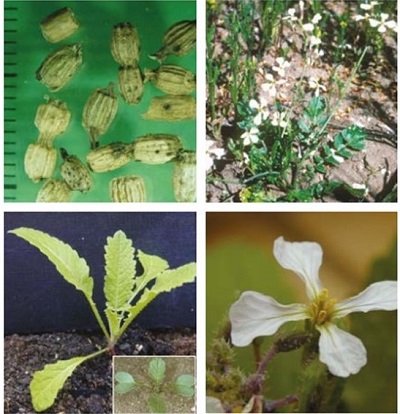
It is an annual, growing to 1m tall, with roughly hairy stems. The leaves have toothed lobes near the stem and a large lobe at the tip. There is a branched tap root.
Key features
Plant: The teeth on the edges of the upper leaves are blunt.
Fruit: The pod appears beaded as it shrinks around the seeds. It has a long beak and breaks easily at the joints.
Lookalikes
It is similar to charlock, as both have roughly hairy stems.

Location and life cycle
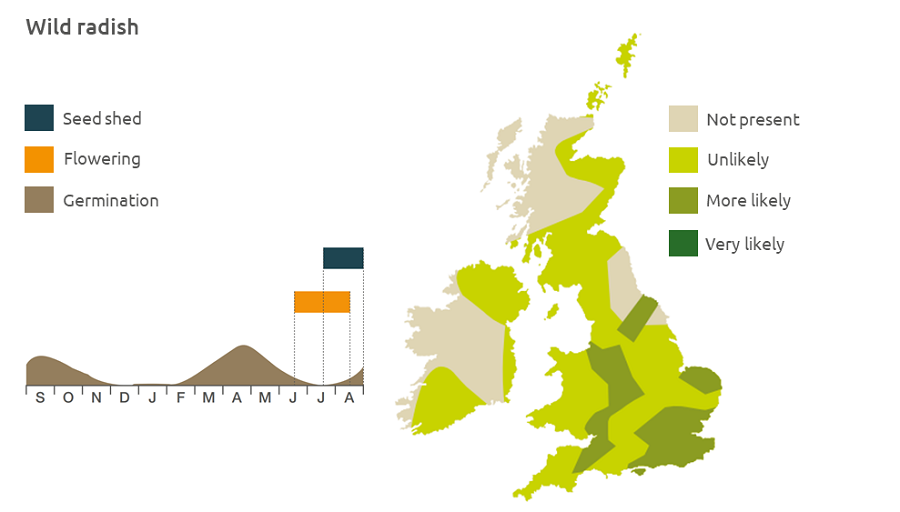
Geographic distribution
Wild radish is found in arable fields, waste ground and paths up to an altitude of 380 m.
Soil type
It prefers lime-free but nutrient-rich sandy and loam soils.
Seed statistics
- Seed longevity: >5 years
- Germination depth: 5 cm
- Seed weight: 6.67 mg
- Seeds/head: 3–10
- Seeds/plant: 160
Management
For advice on herbicides, please speak with your agronomist or adviser.
When was this information last updated?
This page is based on content from the encyclopaedia of arable weeds publication. Since it was first released in 2008, the publication has been redesigned several times but not revised. However, it remains a good foundation for general information on the distribution and biology of weeds.

