- Home
- Knowledge library
- Distribution and biology of knapweed in the UK
Distribution and biology of knapweed in the UK
Knapweed is a broad-leaved weed that is relatively common in older pastures and margins. Find out how to identify and control it.
Overview
Knapweed (Centaurea nigra) is more common in older pastures and is usually found on the margins of arable land. Although the plant dies back overwinter it is a perennial. Plants mainly reproduce by seed, which may survive for several years, if they survive predation by insects or small mammals. Plants may reproduce vegetatively if side shoots become detached from the parent plant.
- It has value to biodiversity
Description
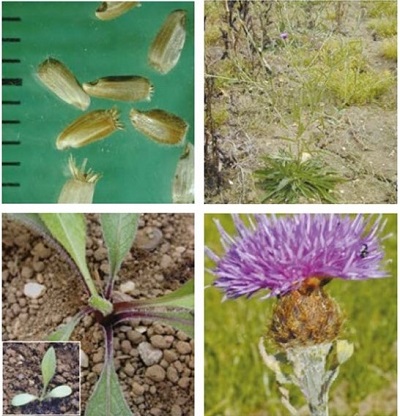
It is a downy, perennial dicotyledon, with upright, tough, usually branched stems, 30–60 cm tall. It has a rosette of leaves at the base and purple thistle-like flowerheads.
Key features
Young plant: The first true leaves have a dark colour.

Location and life cycle
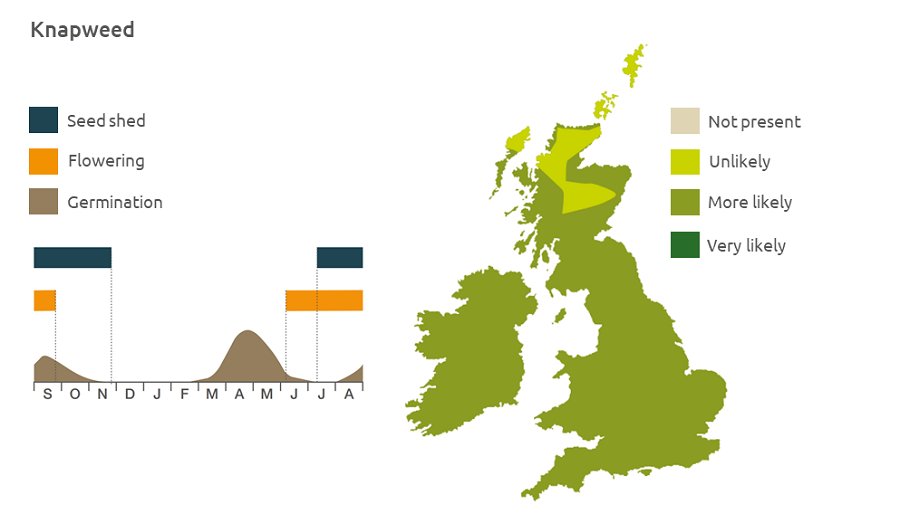
Geographic distribution
Knapweed grows at altitudes of up to 600 m in waste ground, field margins and roadsides, meadows and pastures.
Soil type
It can tolerate a wide range of soils, but prefers unmanured sites.
Seed statistics
- Seed longevity: 1–5 years
- Seed weight: 2.5 mg
- Seeds/flower: 1
- Seeds/plant: Up to 1,000
Management
It does not persist in cultivated soils and is readily controlled with glyphosate in uncropped breaks.
For advice on herbicides, please speak with your agronomist or adviser.
When was this information last updated?
This page is based on content from the encyclopaedia of arable weeds publication. Since it was first released in 2008, the publication has been redesigned several times but not revised. However, it remains a good foundation for general information on the distribution and biology of weeds.

