- Home
- Knowledge library
- Distribution and biology of garlic mustard in the UK
Distribution and biology of garlic mustard in the UK
Garlic mustard is a broad-leaved weed that can be found in field margins and hedgerows. Find out how to identify and control it.
Overview
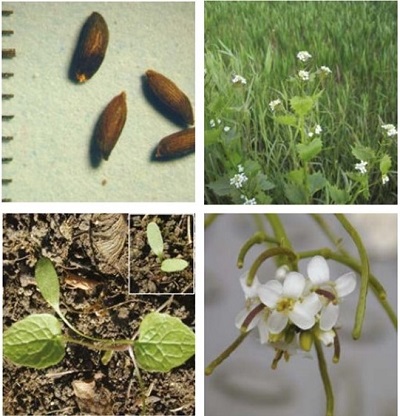
Garlic mustard (Alliaria petiolata) grows in field margins and hedgerows and does not tolerate cultivation or crop competition in arable fields. It overwinters as a rosette of small leaves. The seeds may remain dormant for 18 months or longer.
Description
It is a biennial or perennial dicotyledon, 20–120 cm tall. The stem is upright and much branched with heart-shaped to triangular, shiny and strongly veined leaves. Up to 30 small white flowers with four petals form at the top of the flower stalk.
Key features
Plant: The leaves smell of garlic when crushed.

Location and life cycle
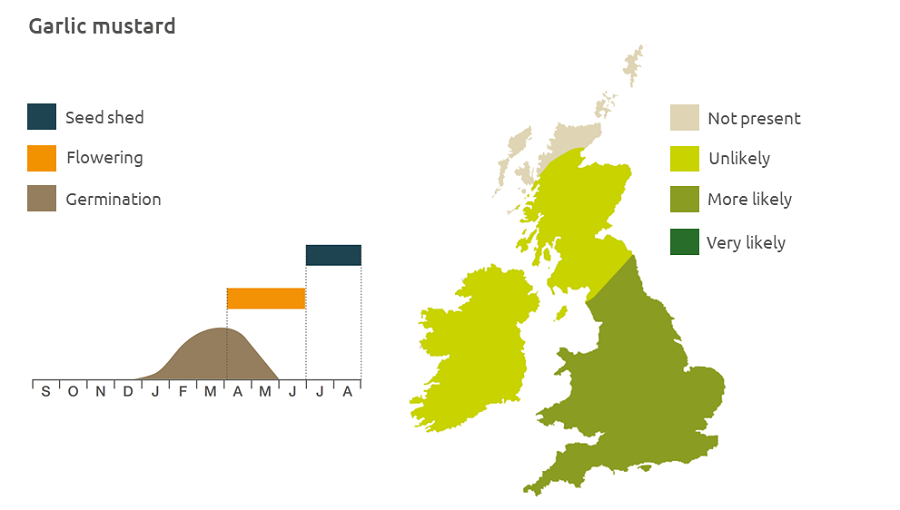
Geographic distribution
Generally a lowland plant, garlic mustard inhabits a wide range of habitats, including hedgerows, waste ground, farmyards and gardens.
Soil type
It prefers fertile moist soils but can grow on all but the most acidic.
Seed statistics
- Seed longevity: >5 years
- Seed weight: 2.5 mg
- Seeds/flower: 20
Management
Care should be taken to reduce seed returning to the seedbank.
For advice on herbicides, please speak with your agronomist or adviser.
When was this information last updated?
This page is based on content from the encyclopaedia of arable weeds publication. Since it was first released in 2008, the publication has been redesigned several times but not revised. However, it remains a good foundation for general information on the distribution and biology of weeds.

