- Home
- Knowledge library
- Distribution and biology of common fumitory in the UK
Distribution and biology of common fumitory in the UK
Common fumitory is a widespread broad-leaved arable weed. Find out how to identify and control it.
Overview
Common fumitory (Fumaria officinalis) is widespread on arable land. It mainly germinates in spring and can set seed in one year. It can be self-fertile or can cross-fertilise.
- It has value to biodiversity
Description
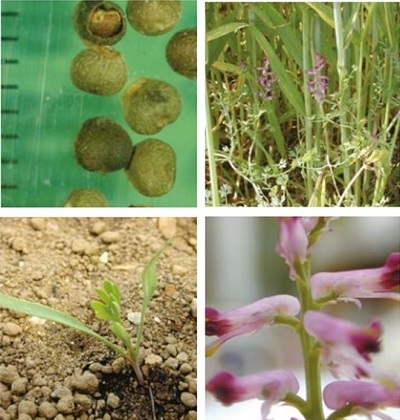
It is a slender, hairless, semi-upright or sprawling, branched annual dicotyledon, growing up to 40 cm tall. The smooth leaves are divided, feathery and slightly greyish in colour. The flower stems have many pinkish lipped flowers, 7–8 mm long and tipped with dark purple-red.
Key features
Plant: The sap is colourless.
Flower: The sepal is less than half the flower length. There are often more than 20 flowers on a flowering spike.
Fruit: It is shaped like a flattened globe.

Location and life cycle
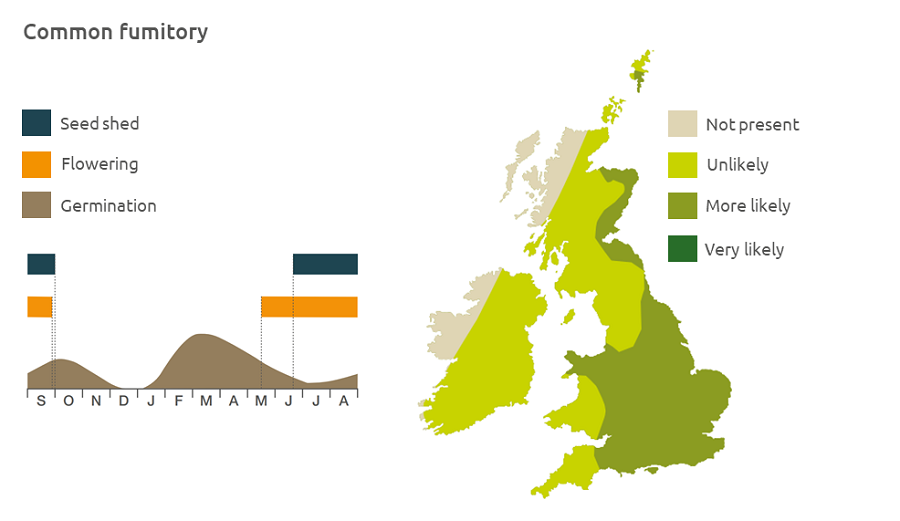
Geographic distribution
Common fumitory is a lowland plant, growing up to an altitude of 300m. It appears in winter and Spring crops and may be increasing in fields of winter cereals in the north of England and in Scotland where there is poor control by residual herbicides.
Soil type
It prefers nutrient-rich chalky loams with good water availability and is an indicator of good soil conditions.
Seed statistics
- Seed longevity: >5 years
- Seed weight: 4 mg
- Seeds/flower: 1
- Seeds/plant: 1,600
Management
For advice on herbicides, please speak with your agronomist or adviser.
When was this information last updated?
This page is based on content from the encyclopaedia of arable weeds publication. Since it was first released in 2008, the publication has been redesigned several times but not revised. However, it remains a good foundation for general information on the distribution and biology of weeds.

