Grass identification
The information here is to help you learn how to identify grass species. Find information, diagrams and images to help.
Back to: Choosing the correct grass species for a grassland reseed
Summary of grass characteristics
It is important to identify what species you currently have in the sward to decide what you need to do to improve it.
Summary of the typical performance of different grass species
| Perennial ryegrass | Italian ryegrass | Hybrid ryegrass | Timothy | Cocksfoot | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diploid | Tetraploid | Diploid | Tetraploid | ||||
| Grazing DM yield (t/ha) | 10.5 | 10.5 | - | - | - | 11.4 | - |
| Grazing D-value | 75.9 | 76.3 | - | - | - | 72.1 | - |
| Silage DM yield (t/ha) | 15.2 | 15.5 | 18.1 | 18.2 | 16.3 | 13.8 | 15.3 |
| Silage D-value | 73.4 | 73.7 | 70.8 | 71.8 | 70.7 | 64.3 | 70.5 |
| Ground cover (1=poor, 9=good) | 6.6 | 5.8 | 3.8 | 6 | 4.2 | 5.3 | 6.3 |
| Winter hardiness (1=poor, 9=good) | 6.5 | 6.7 | 6.8 | 7 | 7.1 | 7.0 | 5.5 |
| Suitable for | Five-to-six-year leys Grazing Silage |
Two-year leys Silage |
Three-to-four-year leys Silage Rotational cattle grazing |
Wetter soil Extensive grazing |
Dry soils Silage |
||
Please select the triangles to expand the text and see the images.
- Most effort by plant breeders has concentrated on PRG
- Establishes rapidly, even from autumn sowing
- High yields in first harvest year
- High sugar content makes it good for silage-making
- Produces dense and persistant swards and is useful for long-term leys and establishing permanent pasture
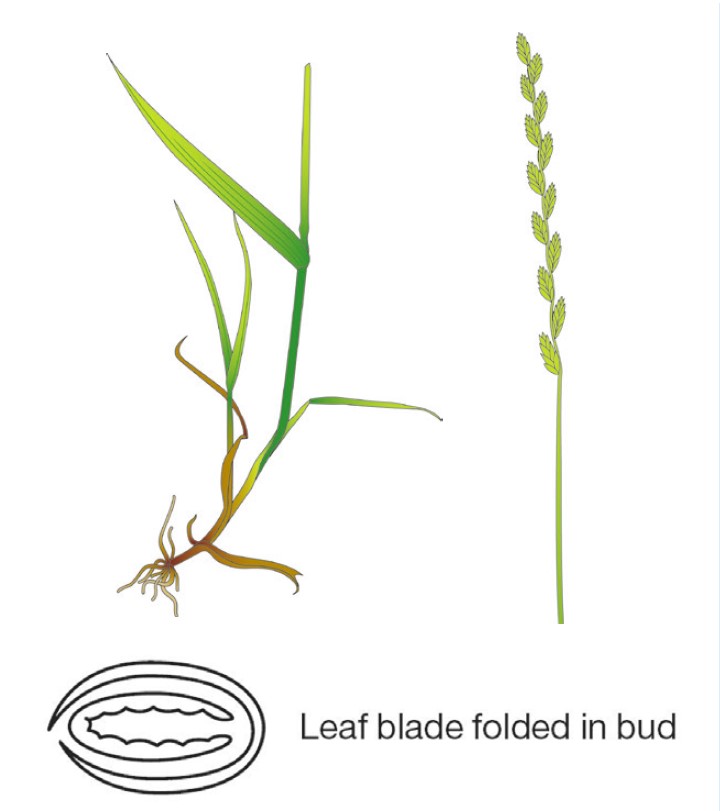
Identification tips
- Large, dark green, tufted plant
- Hairless leaf blades folded in shoot
- Shoots at the base of the plant have a red-purple colour
- Flower head is flattened, with spikelets on opposite sides of the stem
- Spikelets are awnless, unlike Italian ryegrass
Photograph courtesy and copyright of Oliver Seeds.
- Produces heavy crops of silage or hay
- Useful for short-term leys of one to three years
- Long growing season gives oppurtunity for ‘early-bite’ grazing, followed by leafy hay or silage cut
- Relatively easy to establish
Identification tips
- Large, stout, fast-growing and densely tufted plant with red bases to the shoots
- Dark green, hairless leaf blades rolled in stem
- Flower head is flattened with spikelets arranged alternateley on opposite sides of the stem
- Spikelets are awned, unlike perennial ryegrass
Photograph courtesy and copyright of Oliver Seeds.
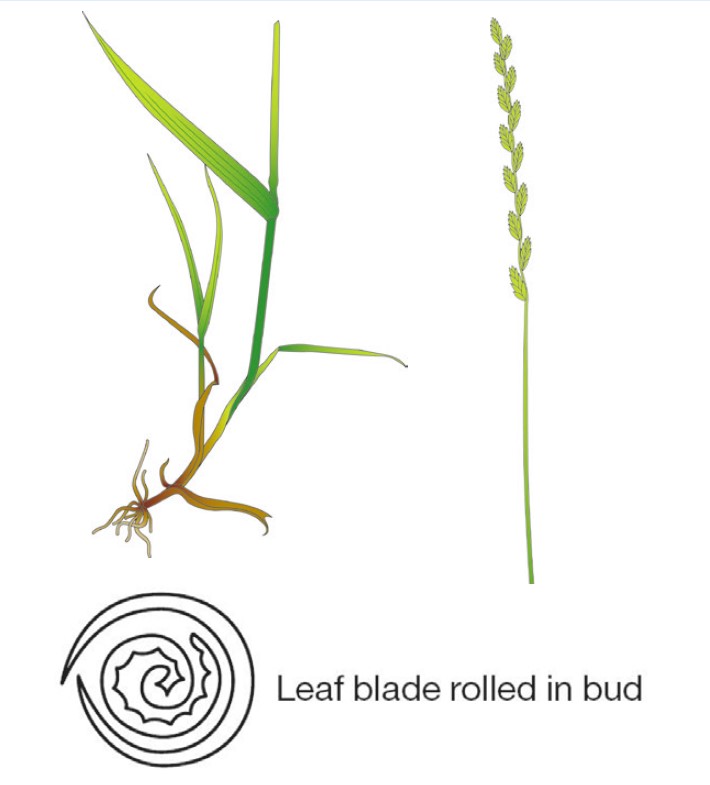

- Better ground cover and longer-lived than IRG
- Good winter hardiness and disease resistance
- Midseason digestibility better than IRG, but poorer than PRG
- First-year yields lower than IRG, but yield improves in second and third year
- Potentially more drought-resistant than IRG
- Suits being grown along with red clover

Photography courtesy and copyright of NIAB.
- Grows at lower temperatures than ryegrass so can be good for early-season grazing, especially in cold, late springs
- Good midseason growth can fill the gap when ryegrass growth falters
- Good winter hardiness and ground cover
- Can be slow to establish and yields are likely to be lower than PRG
- Best used in cooler, wetter areas
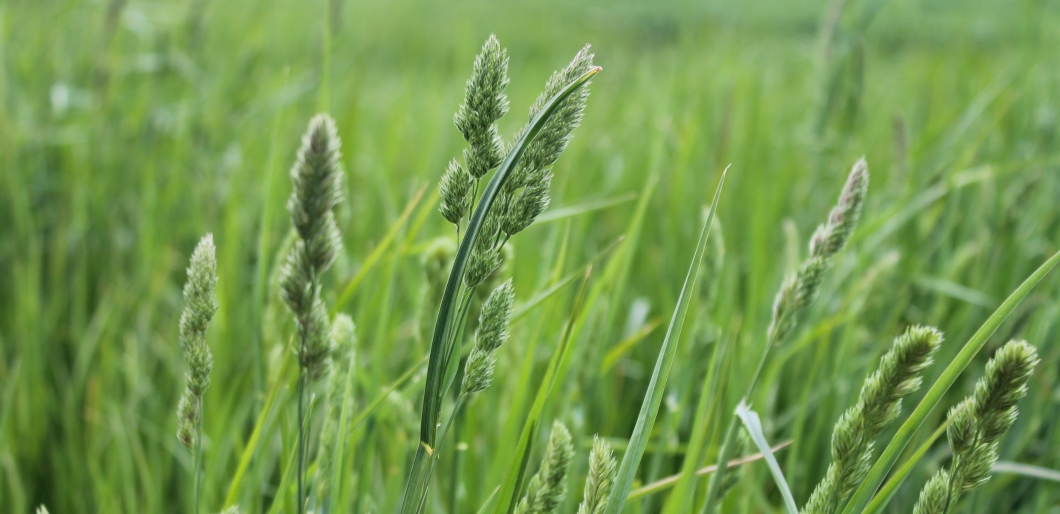
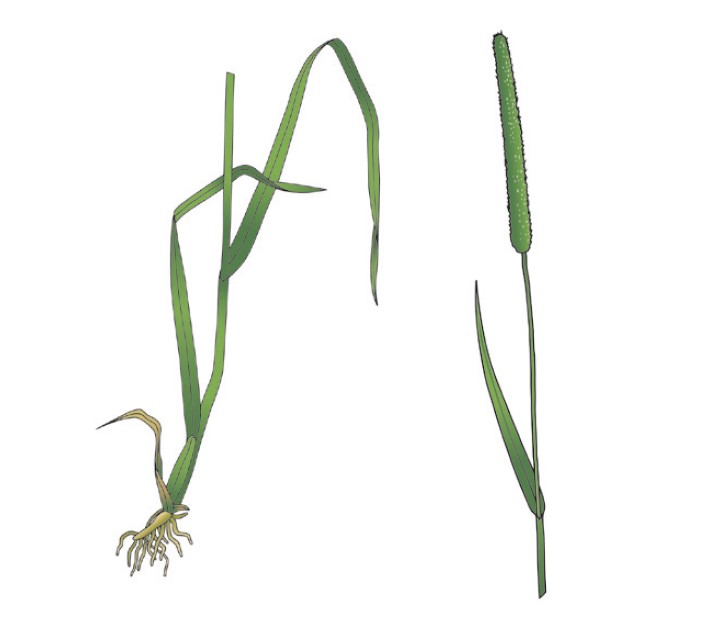
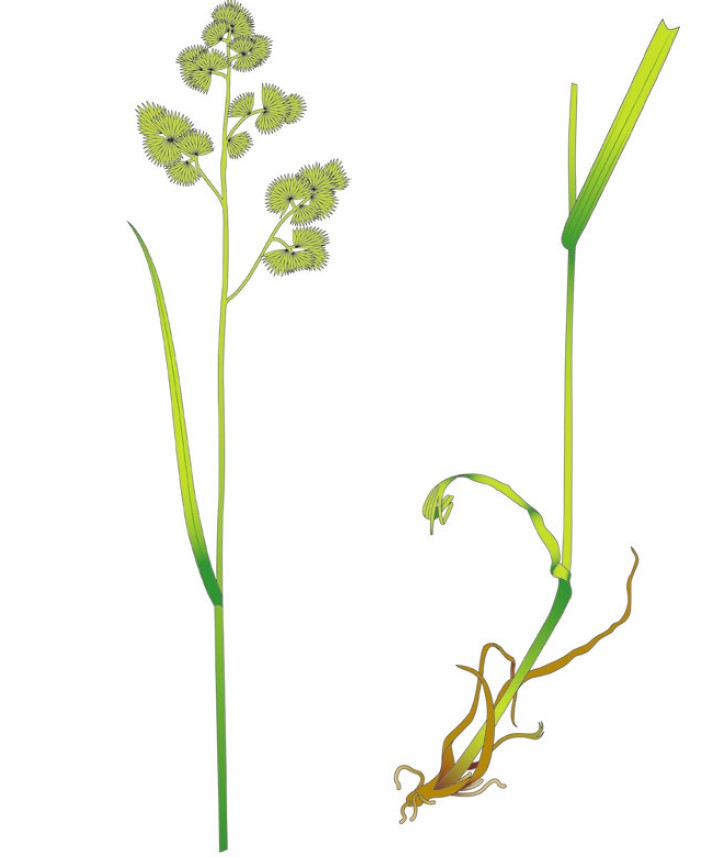
Identification tips
- A light greyish-green, tuft-forming plant with short rhizomes
- Leaves are rolled in the bud and have a twisted top tapering to a point
- Young leaves are soft and hairless
- Bottom of the stem is generally bulbous
- The flower head looks like a cat’s tail and has two needles on every spikelet
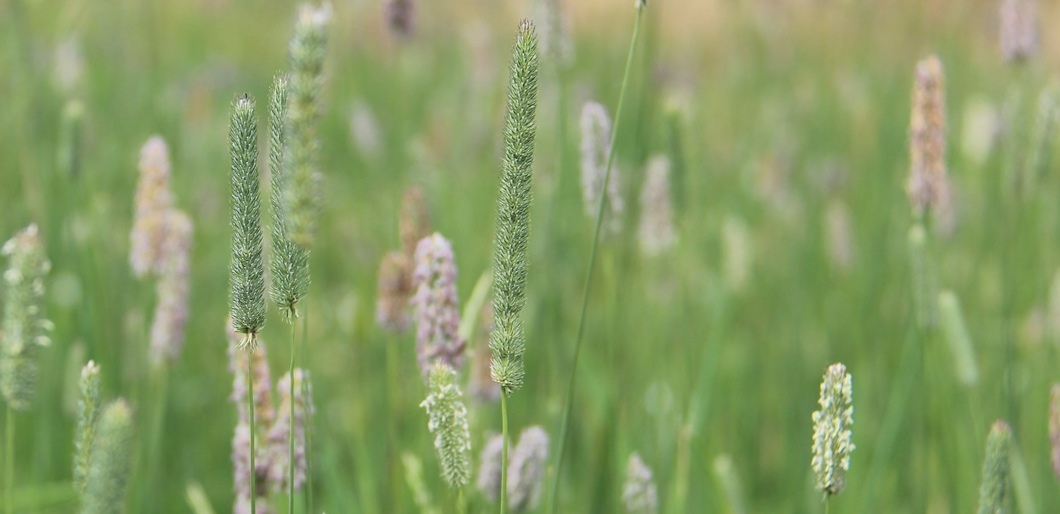

Photograph courtesy and copyright of Oliver Seeds.

- Drought-tolerant
- Hard-wearing
- Good summer production, especially in dry conditions
- Lower quality and yields than PRG
- Early heading date
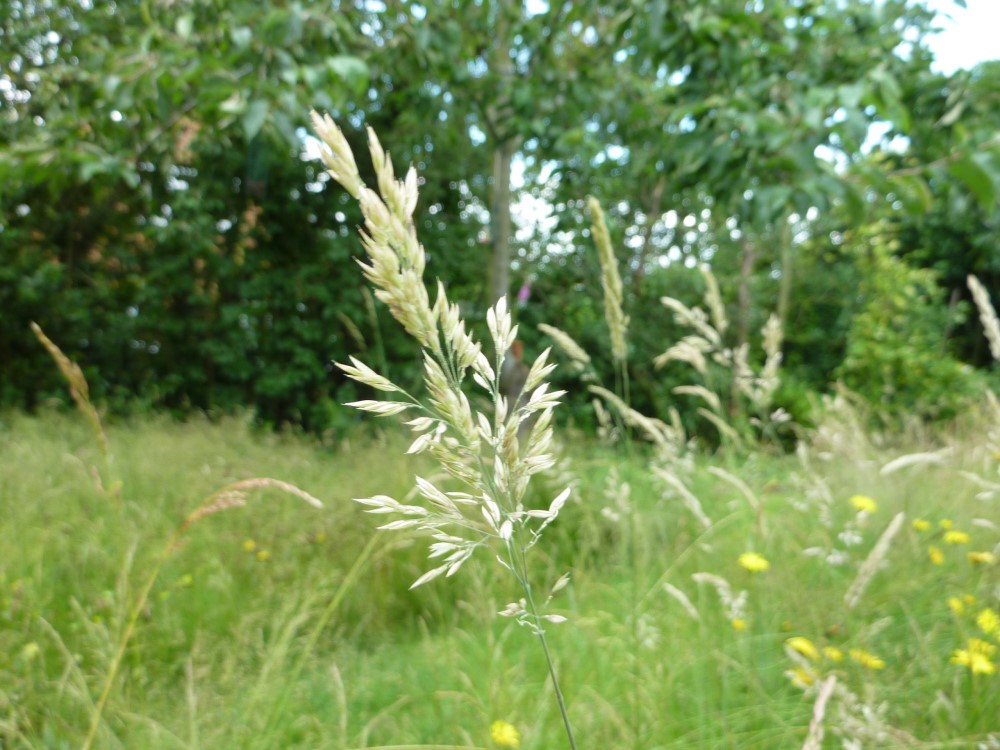
Identification tips
- Large, densely tufted plant
- Often forming large tussocks
- Coarse-looking grass often bluish-green in colour, with white ligules
- Dull green or greyish-green leaf blade which is rough, broad and sharply pointed
- Folded-in flattened shoot
- Strongly keeled
- Flower head is one-sided, usually as a triangular cluster
- Spikelets are small, flattened and condensed into oval-shaped clusters
Photograph courtesy and copyright of Oliver Seeds.
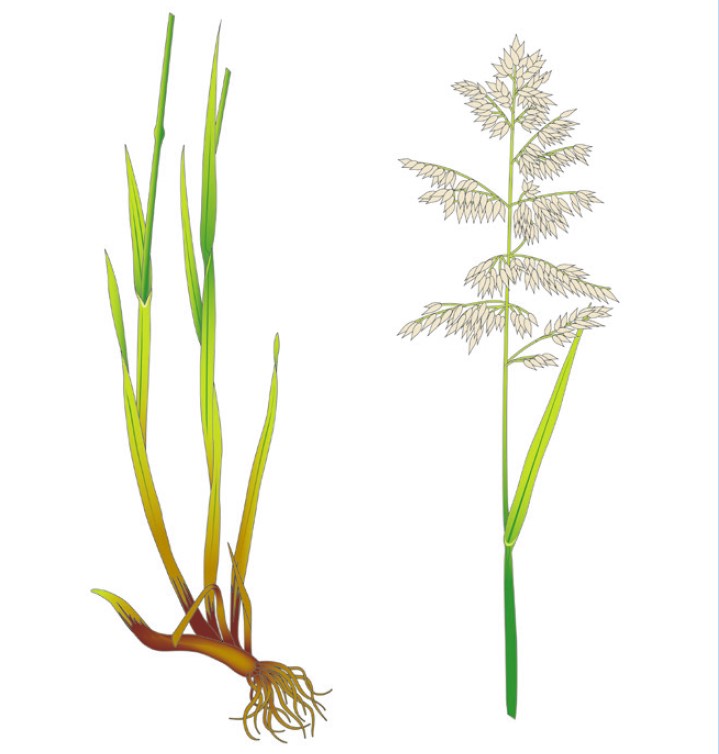
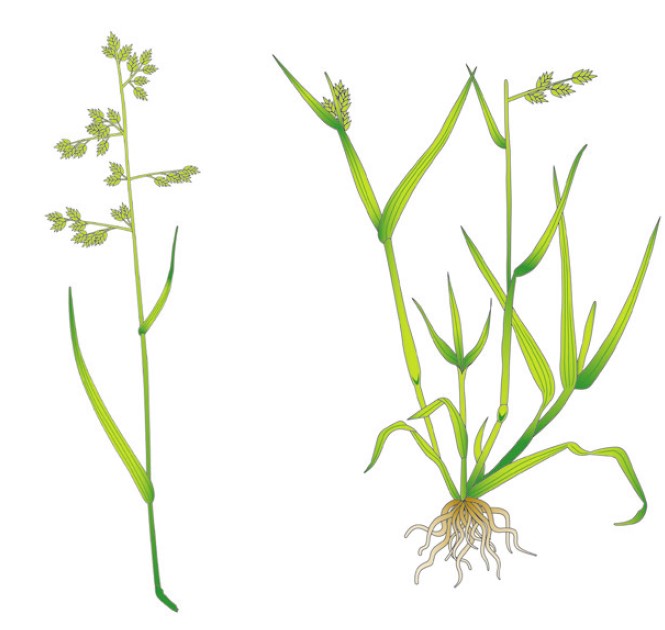
Identification tips
- Tufted, very hairy plant
- Pale greyish-green leaves narrowing to a fine point
- Rolled leaves in the stem, very hairy and velvety to the touch
- Basal leaf sheaths have pinkish-red stripes
- Flower heads are whitish, pale green, pinkish or purple
- No rhizomes
Photograph courtesy and copyright of Oliver Seeds.

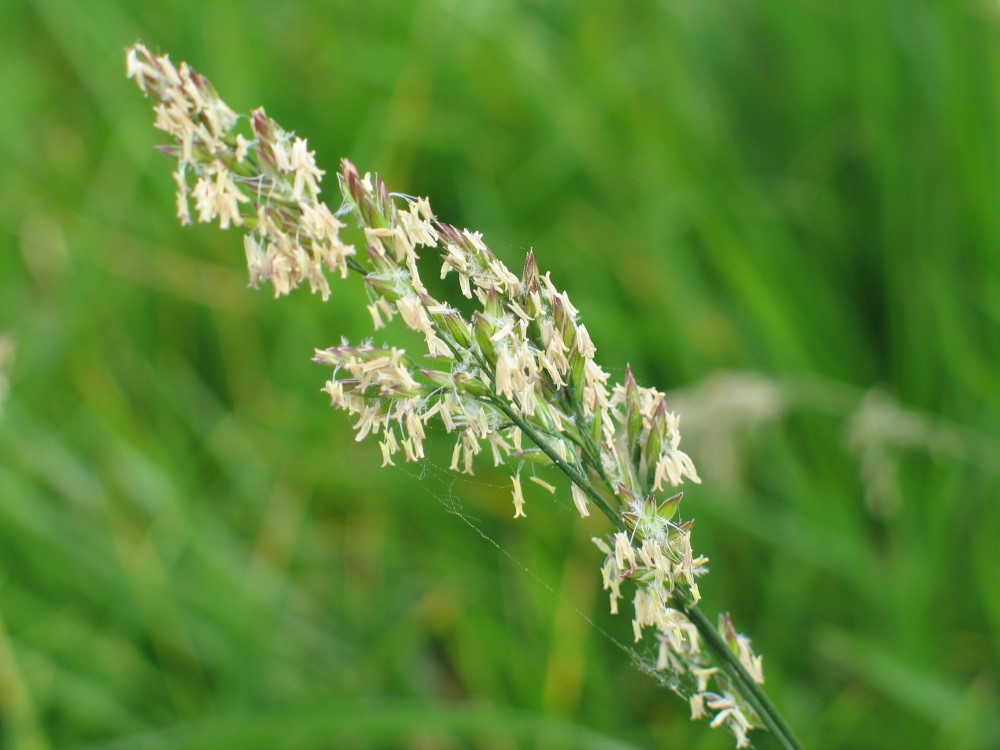
Identification tips
- Small, pale green, loosely tufted plant
- Blade often crinkled or puckered and hairless, with boat-shaped tip
- Blade is slightly keeled, with ‘tramlines’, and is folded in shoot
- Flowering head is branched and spreading, triangular in outline
- Spikelets are small and awnless
b.jpg)
- One year of production only
- Very high-yielding
- Used for early grazing and cutting, but quality can be poor
- Tall or meadow fescues can be sown
- Can be crossed with ryegrasses to produce festulolium (see below)
- Yields less than ryegrass
- Useful in hill grazing or low-intensity situations

Red Fescue photograph courtesy and copyright of Oliver Seeds.
Meadow Fescue photograph courtesy and copyright of Oliver Seeds.
- A ryegrass/fescue hybrid mix
- Lower yields than ryegrass and reduced digestibility with the addition of fescue strains
- Varieties being developed for drought tolerance, to increase water infiltration rates and reduce risk of flooding

Photography courtesy and copyright of Oliver Seeds.
Topics:
Sectors:
Tags:






