- Home
- Knowledge library
- Distribution and biology of sugar beet volunteer weeds in the UK
Distribution and biology of sugar beet volunteer weeds in the UK
Sugar beet can be a volunteer weed in fields of sown beet or other crops. Find out how to identify and control it.
Overview
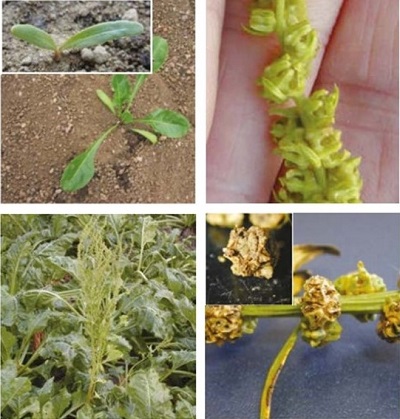
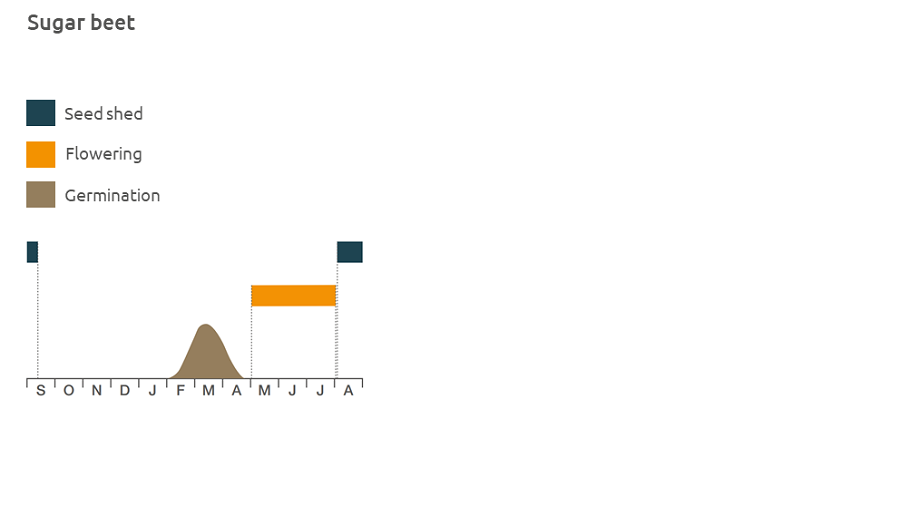
Weed beet (Beta vulgaris) are any unwanted sugar beet growing within and between the rows of sown beet or other crops. They grow from groundkeepers or from seed shed by bolting crop plants or other weed beets. As seedlings, they are indistinguishable from sugar beet. Sugar beet which germinates in spring usually overwinters as a leafy rosette before flowering in the following year. However in some cases the plants flower in the first year (in a crop these beets are known as bolters) and are prolific seed producers.
Description
It is a large biennial that grows to 1.8 m tall, but in the first year has a rosette of large dark-green oval leaves. The cultivated form of beet has a large tap root.
Key features
Fruit: It is distinguished from other beets by thicker leaves and a large bulbous tap root.

Location and life cycle
Geographic distribution
Sugar beet is found usually in lowland areas as a volunteer from previous cropping.
Soil type
It is found on light arable soils.
Seed statistics
- Seeds/flower: 1
- Seeds/plant: 10,000
Management
Crops containing bolters should be harvested as early as possible to reduce the production of viable seeds.
For advice on herbicides, please speak with your agronomist or adviser.
When was this information last updated?
This page is based on content from the encyclopaedia of arable weeds publication. Since it was first released in 2008, the publication has been redesigned several times but not revised. However, it remains a good foundation for general information on the distribution and biology of weeds.

