- Home
- Knowledge library
- Distribution and biology of ragwort in the UK
Distribution and biology of ragwort in the UK
Ragwort is uncommon as an arable weed but may be found in fallows and field margins. Find out how to identify and control it.
Overview
Ragwort (Senecio jacobaea) can be abundant in poor pasture and wasteland, particularly on sandy free-draining soils. It is rarely found as an arable weed, but does establish in fallows and field margins. Seedlings germinating in autumn can overwinter as leafy plants. The plant may take more than two years to flower. Seed is not dispersed far from the parent plant, but can survive grazing and can be transported by sheep. The flowering shoots die by winter.
- It has value to biodiversity
Description
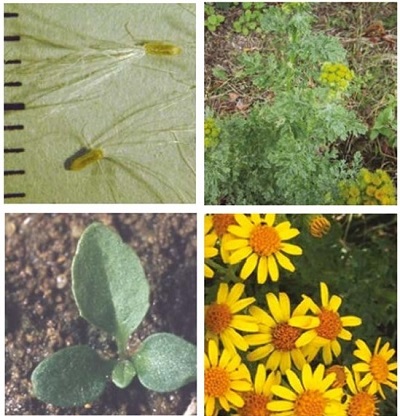
It is a medium-tall, hairless biennial, not very branched, with a basal rosette of grey-green, roundly divided leaves. The flowerhead has groups of yellow daisy-like flowers.
Key features
Plant: The plant contains the poison jacobine, which is fatal to livestock.

Location and life cycle
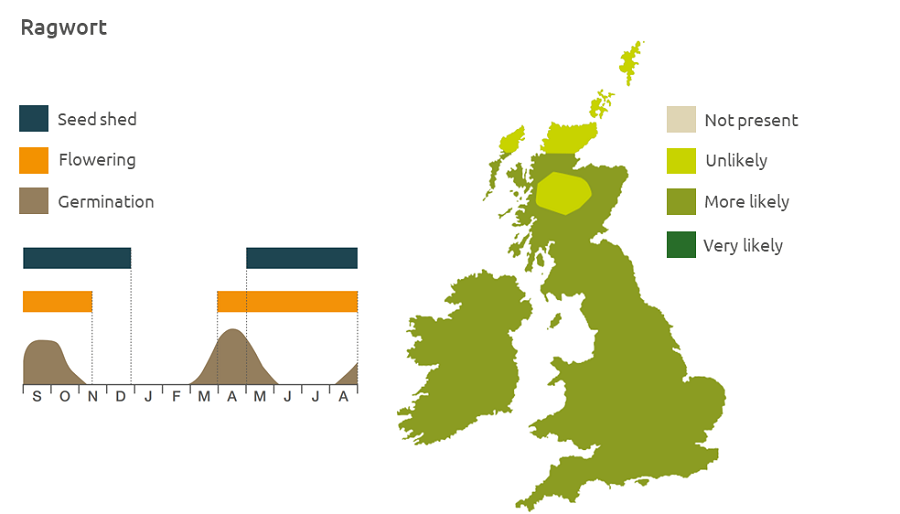
Geographic distribution
Ragwort is commonly found on grasslands and neglected land, headlands and verges. Growing to an altitude of nearly 700 m.
Soil type
It grows in a wide range of soils, between pH 5 and 7.
Seed statistics
- Seed longevity: >5 years
- Seed weight: 0.2 mg
- Seeds/head or capsule: 100
- Seeds/plant: 50,000–60,000
Management
Dense grass swards which are not over-grazed reduce establishment.
For advice on herbicides, please speak with your agronomist or adviser.
When was this information last updated?
This page is based on content from the encyclopaedia of arable weeds publication. Since it was first released in 2008, the publication has been redesigned several times but not revised. However, it remains a good foundation for general information on the distribution and biology of weeds.

