- Home
- Knowledge library
- Distribution and biology of pineappleweed in the UK
Distribution and biology of pineappleweed in the UK
Pineappleweed is often dispersed on boots and tyres, and smells of pineapple when bruised. Find out how to identify and control it.
Overview
Pineappleweed (Matricaria discoides) is usually found on tracks and in gateways, but also encroaches onto arable land, preferring compacted soils. It is found in both winter and spring crops and can become a nuisance in perennial crops where there is a lot of vehicle movement. Seedlings germinating in autumn can overwinter. Spring-germinating plants can set seed within 40–50 days. Seeds are usually dispersed on boots and tyres.
- It has value to biodiversity
Description
It is an upright, stiffly branched, bushy annual dicotyledon, 5–40 cm tall. The leaves are finely divided and feathery. Flowers are like other mayweeds but lack the white outer petals.
Key features
Plant and flower: It smells strongly of pineapple when bruised.
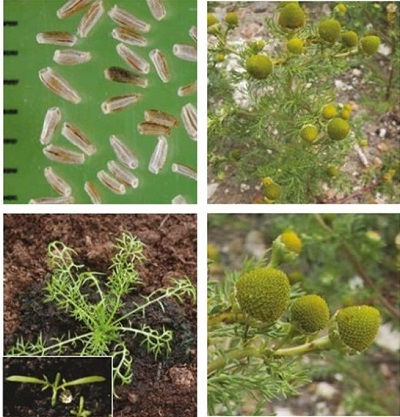

Location and life cycle
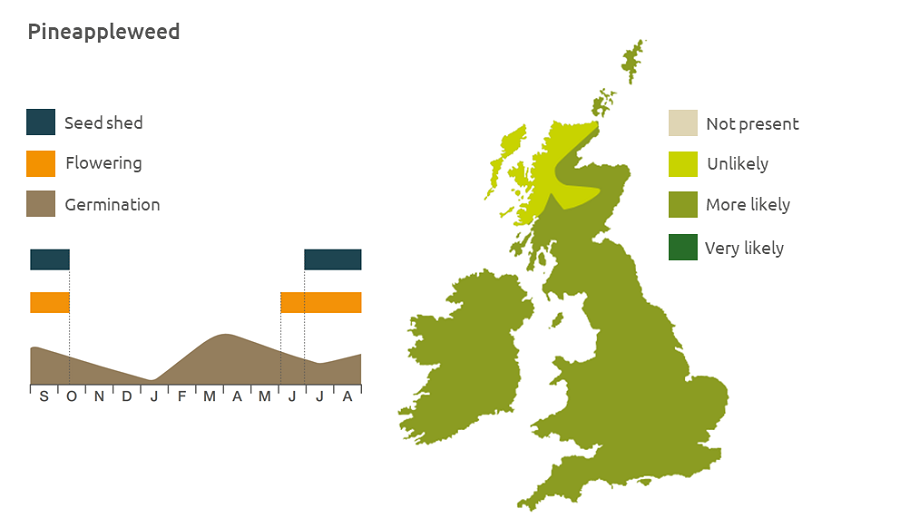
Geographic distribution
Pineappleweed grows in all arable crops and on compacted soil or habitats with a wide proportion of bare ground. It is usually a lowland species but has been found at an altitude of 530 m.
Soil type
It is restricted to damp and nutrientrich sandy soils and loams, pH >5.
Seed statistics
- Seed longevity: >5 years
- Germination depth: 5 cm
- Seed weight: 0.18 mg
- Seeds/head: 50–400
- Seeds/plant: 0–6,000
Management
It is readily controlled with herbicides and in-crop cultivation.
For advice on herbicides, please speak with your agronomist or adviser.
When was this information last updated?
This page is based on content from the encyclopaedia of arable weeds publication. Since it was first released in 2008, the publication has been redesigned several times but not revised. However, it remains a good foundation for general information on the distribution and biology of weeds.

