- Home
- Knowledge library
- Distribution and biology of nipplewort in the UK
Distribution and biology of nipplewort in the UK
Nipplewort is a common weed of cereals. Find out how to identify and control it.
Overview
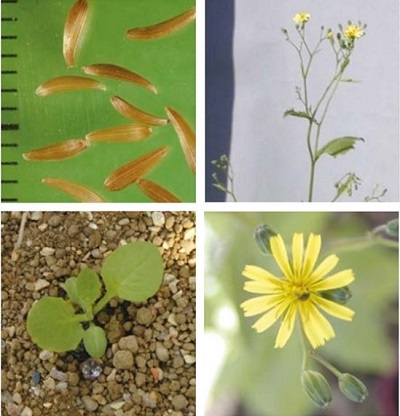
Nipplewort (Lapsana communis) is common on cultivated land, particularly in cereals, though its population is probably decreasing. Nipplewort is more common in winter cereals, but is also found in spring crops in colder, wetter areas. It has relatively large seeds which may contaminate crop seeds. Autumn-germinating seeds can overwinter as rosettes and become very tall plants. Its form varies widely, depending on location.
Description
It is a hairy, upright, branched, leafy annual or biennial dicotyledon, 30–120 cm tall. Basal leaves are oval and toothed but the upper stem leaves are spear-shaped. Flowers are yellow, small and look similar to those of dandelion.
Key features
Plant: The plant has stiff hairs at the base and is smooth above; it is much branched and angular, and fairly loosely rooted.
Flowers: The open spikes of yellow dandelion-like flowers are smaller than those of other yellow composites.

Location and life cycle
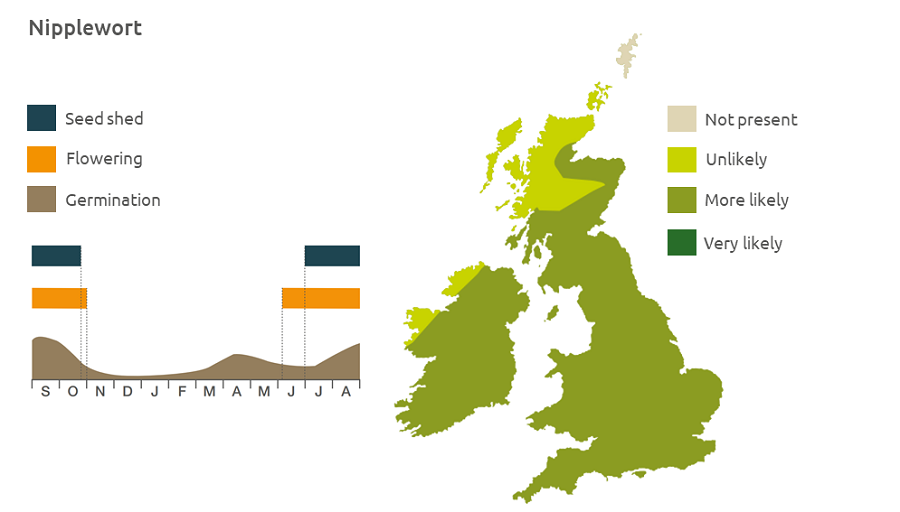
Geographic distribution
Nipplewort is a lowland species found on arable land and other bare disturbed ground up to an altitude of about 300 m.
Soil type
It occurs in loams and clays that are nutrient-rich with moderate nitrogen and often damp.
Seed statistics
- Seed longevity: >5 years
- Seed weight: 2 mg
- Seeds/head: 30
- Seeds/plant: 600–700
Management
Nipplewort is controlled by a range of herbicides suitable for broad-leaved weeds.
For advice on herbicides, please speak with your agronomist or adviser.
When was this information last updated?
This page is based on content from the encyclopaedia of arable weeds publication. Since it was first released in 2008, the publication has been redesigned several times but not revised. However, it remains a good foundation for general information on the distribution and biology of weeds.

