- Home
- Knowledge library
- Distribution and biology of fool’s parsley in the UK
Distribution and biology of fool’s parsley in the UK
Fool’s parsley is a weed of arable land. Find out how to identify and control it.
Overview
Fool’s parsley (Aethusa cynapium) plants germinate in spring and die back after flowering.
Description
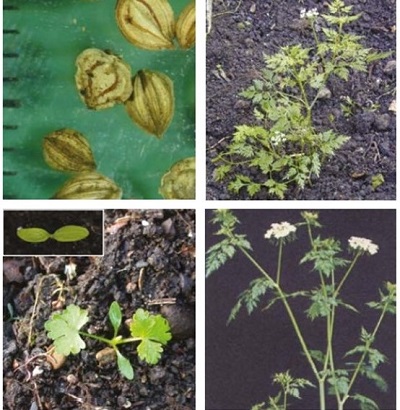
It is an annual, very variable in height, up to 50cm tall but usually only about 20 cm on arable land. The leaves are repeatedly divided, similar to those of parsley. The small white flowers are in flat-topped flowerheads.
Key features
Flowers: Fool’s parsley has downward-pointing projections (bracteoles) under each flower.
Lookalikes
Fool’s parsley can be mistaken for wild carrot at the seedling stage. The cotyledons of fool’s parsley are wider and shorter and the first true leaves less finely divided than those of wild carrot.

Location and life cycle
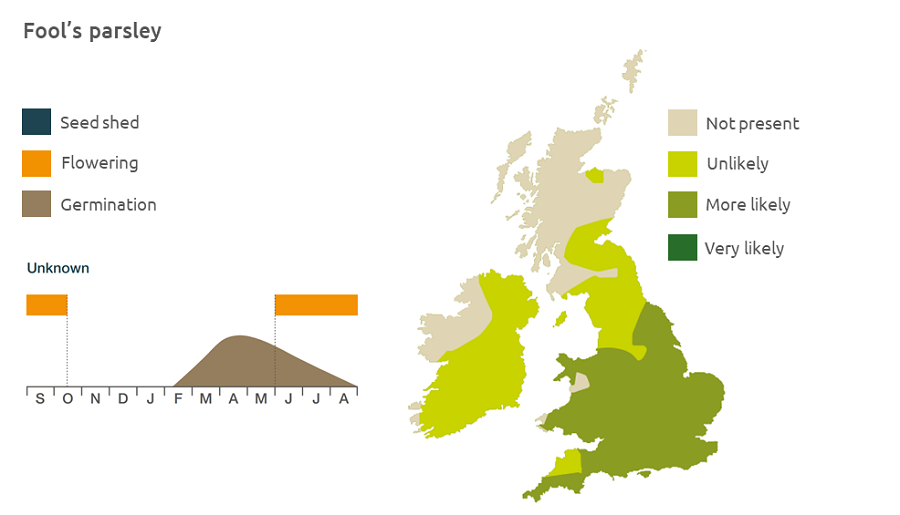
Geographic distribution
Distributed towards the south of Britain, fool’s parsley is found on cultivated lands, in undergrowth and water meadows.
Soil type
It is usually found on nutrient-rich soils, which may be chalky or neutral to alkaline loams.
Seed statistics
- Seed longevity: >5 years
- Seed weight: 2.5 mg
- Seeds/floret: 2
- Seeds/plant: 500
Management
Fool’s parsley can be controlled in arable land by grass breaks of 2–3 years and reduced by growing shading break crops. Seedlings can be successfully harrowed when small.
For advice on herbicides, please speak with your agronomist or adviser.
When was this information last updated?
This page is based on content from the encyclopaedia of arable weeds publication. Since it was first released in 2008, the publication has been redesigned several times but not revised. However, it remains a good foundation for general information on the distribution and biology of weeds.

