- Home
- Knowledge library
- Distribution and biology of black nightshade in the UK
Distribution and biology of black nightshade in the UK
Black nightshade is a common broad-leaved weed of vegetable and spring legume crops. Find out how to identify and control it.
Overview
Black nightshade (Solanum nigrum) is a common weed of vegetable and spring legume crops. Flowers are pollinated by insects and are self-fertile. It germinates in spring and summer, fruiting in the same year. The seeds are distributed by birds. It does not persist in winter crop rotations and where there are large grass breaks.
- Some populations are associated with herbicide resistance
- It has value to biodiversity
Weed Resistance Action Group (WRAG)
Description
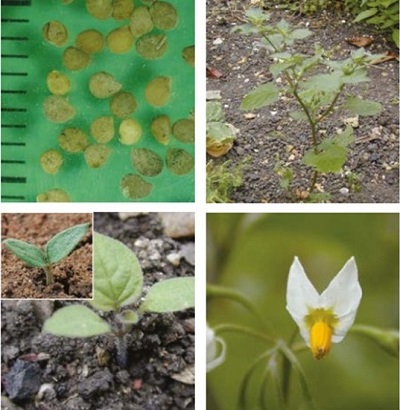
It is a branched, bushy annual plant with dark oval leaves, growing up to 70 cm tall. The flowers resemble white potato flowers and occur in groups of 5 to 10.
Key features
Young plant: The hypocotyls and cotyledons are hairy.
Fruit: The fruit is spherical and glossy black.

Location and life cycle
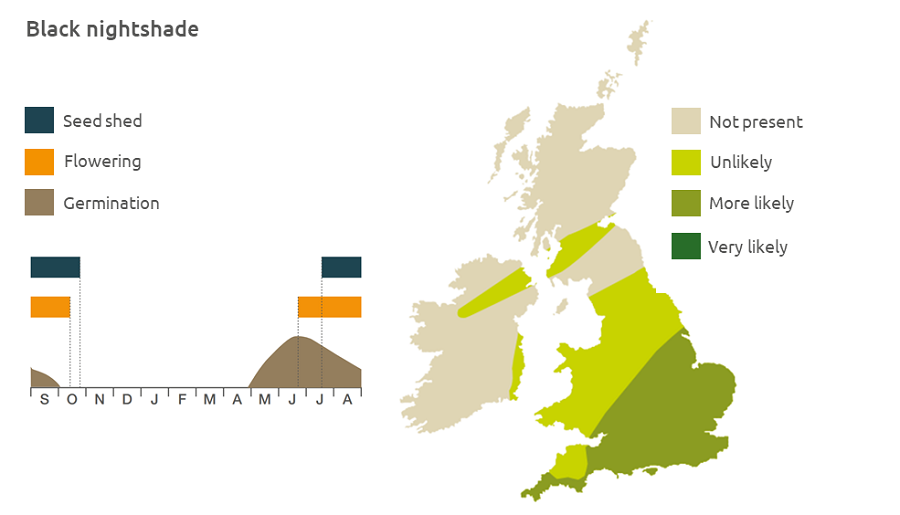
Geographic distribution
Black nightshade is fairly widespread in vegetable crops, gardens, vineyards and on banks and rubbish tips.
Soil type
It prefers loose, free-draining, nutrient-rich soils in the pH range 5 to 7.
Seed statistics
- Seed longevity: >5 years
- Germination depth: 5.5 cm
- Seed weight: 1 mg
- Seeds/flower: 40
- Seeds/plant: 500
Management
There are a number of herbicides available to control black nightshade in winter wheat but it is easier to control the weed in uncropped land. In row crops, use hoes where herbicides are not available.
For advice on herbicides, please speak with your agronomist or adviser.
When was this information last updated?
This page is based on content from the encyclopaedia of arable weeds publication. Since it was first released in 2008, the publication has been redesigned several times but not revised. However, it remains a good foundation for general information on the distribution and biology of weeds.

