- Home
- Knowledge library
- Distribution and biology of black mustard in the UK
Distribution and biology of black mustard in the UK
Black mustard is a broad-leaved weed that can be competitive in winter oilseed rape crops. Find out how to identify and control it.
Overview
Black mustard (Brassica nigra) was formerly cultivated as mustard seed, though it is now rarely grown. Although some early-germinating plants overwinter they are not hardy and seldom survive the winter, so seed germinating in spring is more of a problem in late-sown wheat and spring-sown crops.
- It is particularly competitive in winter oilseed rape
Description
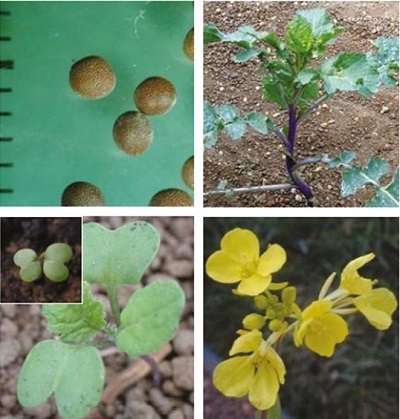
It is a tall, branched, annual dicotyledon, 40–200 cm tall with a bristly lower stem. The flowers are bright yellow.
Key features
Leaves: The leaves are lobed and hairy.

Location and life cycle
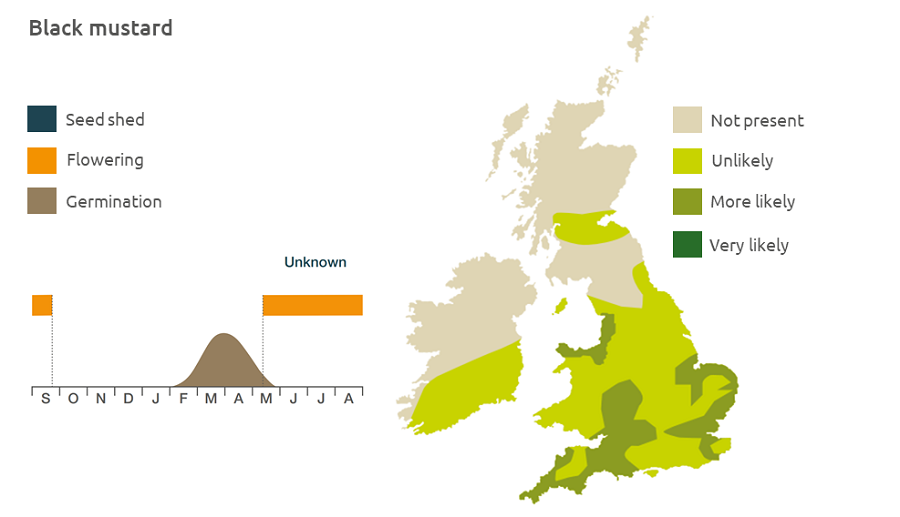
Geographic distribution
Generally a lowland plant, black mustard grows persistently near rivers, in flood plains, in arable field margins and in waste ground.
Soil type
It prefers nutrient-rich and damp clays and silts.
Seed statistics
- Seed longevity: >5 years
- Seed weight: 3.33 mg
- Seeds/plant: 10–100
Management
Use a stale seedbed approach before sowing spring crops. Control seedlings with harrows and established plants with hoeing.
For advice on herbicides, please speak with your agronomist or adviser.
When was this information last updated?
This page is based on content from the encyclopaedia of arable weeds publication. Since it was first released in 2008, the publication has been redesigned several times but not revised. However, it remains a good foundation for general information on the distribution and biology of weeds.

