Dairy fat and protein trade deficits grow in 2020
Wednesday, 26 May 2021
By Kat Jack
Historically, the UK has had a trade deficit for dairy products, importing more than we export. This switched to a trade surplus in volume terms in 2019 and 2020, though we continue to trade at a deficit in value terms. Much of the value in a dairy product comes from its constituents, and so looking at our trade balance in terms of fat and protein can provide valuable insight on demand for milk solids.
In 2020, both the fat and protein trade deficits grew, with the fat deficit up 8% on 2019 and the protein deficit up 2%. However, both these deficits are still considerably smaller than those seen in 2016-2018.
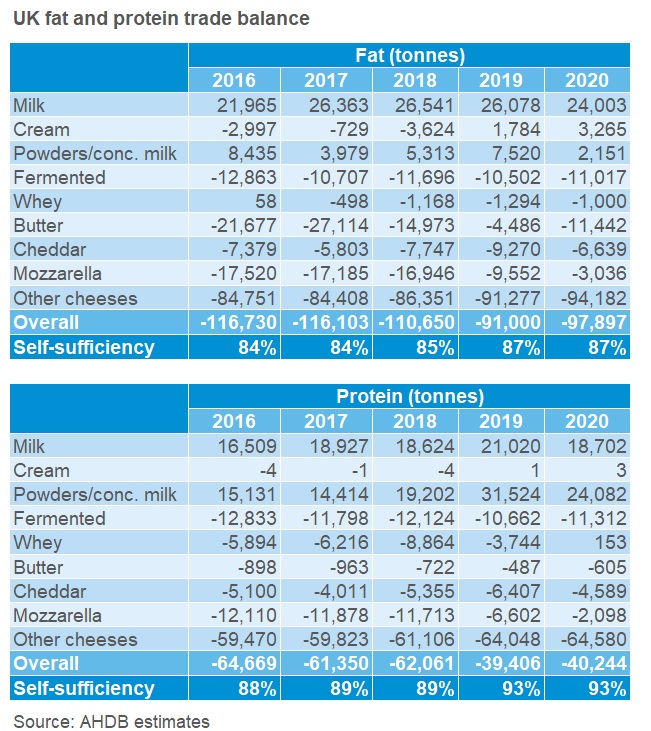
The increased fat trade deficit was partly driven by butter, where the trade deficit increased. High retail demand in the UK kept imports at a similar level to the previous year, and may have kept more domestic product in the country, as we saw reduced exports – though reduced demand from the continent may also have contributed. A reduction in our powder export surplus, particularly for WMP, also contributed to the increased fat deficit.
However, this was counterbalanced by some categories improving, for example Cheddar and Mozzarella had lower fat trade deficits year on year. Mozzarella exports continued to improve on the back of increased production capacity. For Cheddar, both imports and exports were down, but imports more so. For imports this is likely due to reduced foodservice demand in the UK, as the sector usually uses a lot of commodity Irish cheddar. Meanwhile, exports were lower due to reduced demand abroad, but potentially also due to increased domestic demand in the retail sector.
For protein, a substantial drop in the surplus from powders helped drive the growth in the overall deficit. This was down to lower exports of SMP and WMP compared to 2019. On the other hand, Cheddar and Mozzarella had reduced protein deficits in 2020, correlating with their reduced fat deficits. Additionally, whey products went from a protein deficit of 3,740 tonnes in 2019 to a small 150 tonne surplus in 2020, mainly due to lower imports.
Looking forwards, 2021 will bring an interesting year for our trade balance. With increased trade friction putting a damper on exports since January, but the same regulations not set to hit imports until October, this could sway things in favour of an increased deficit. However, this is not yet guaranteed.

Sign up to receive the latest information from AHDB.
While AHDB seeks to ensure that the information contained on this webpage is accurate at the time of publication, no warranty is given in respect of the information and data provided. You are responsible for how you use the information. To the maximum extent permitted by law, AHDB accepts no liability for loss, damage or injury howsoever caused or suffered (including that caused by negligence) directly or indirectly in relation to the information or data provided in this publication.
All intellectual property rights in the information and data on this webpage belong to or are licensed by AHDB. You are authorised to use such information for your internal business purposes only and you must not provide this information to any other third parties, including further publication of the information, or for commercial gain in any way whatsoever without the prior written permission of AHDB for each third party disclosure, publication or commercial arrangement. For more information, please see our Terms of Use and Privacy Notice or contact the Director of Corporate Affairs at info@ahdb.org.uk © Agriculture and Horticulture Development Board. All rights reserved.

