- Home
- Knowledge library
- Identifying how digital dermatitis is transmitted between dairy cows (PhD)
Identifying how digital dermatitis is transmitted between dairy cows (PhD)
Summary
Summary/Key points:
When considering wintin host (animal) infection reservoirs other than within the foot leion:
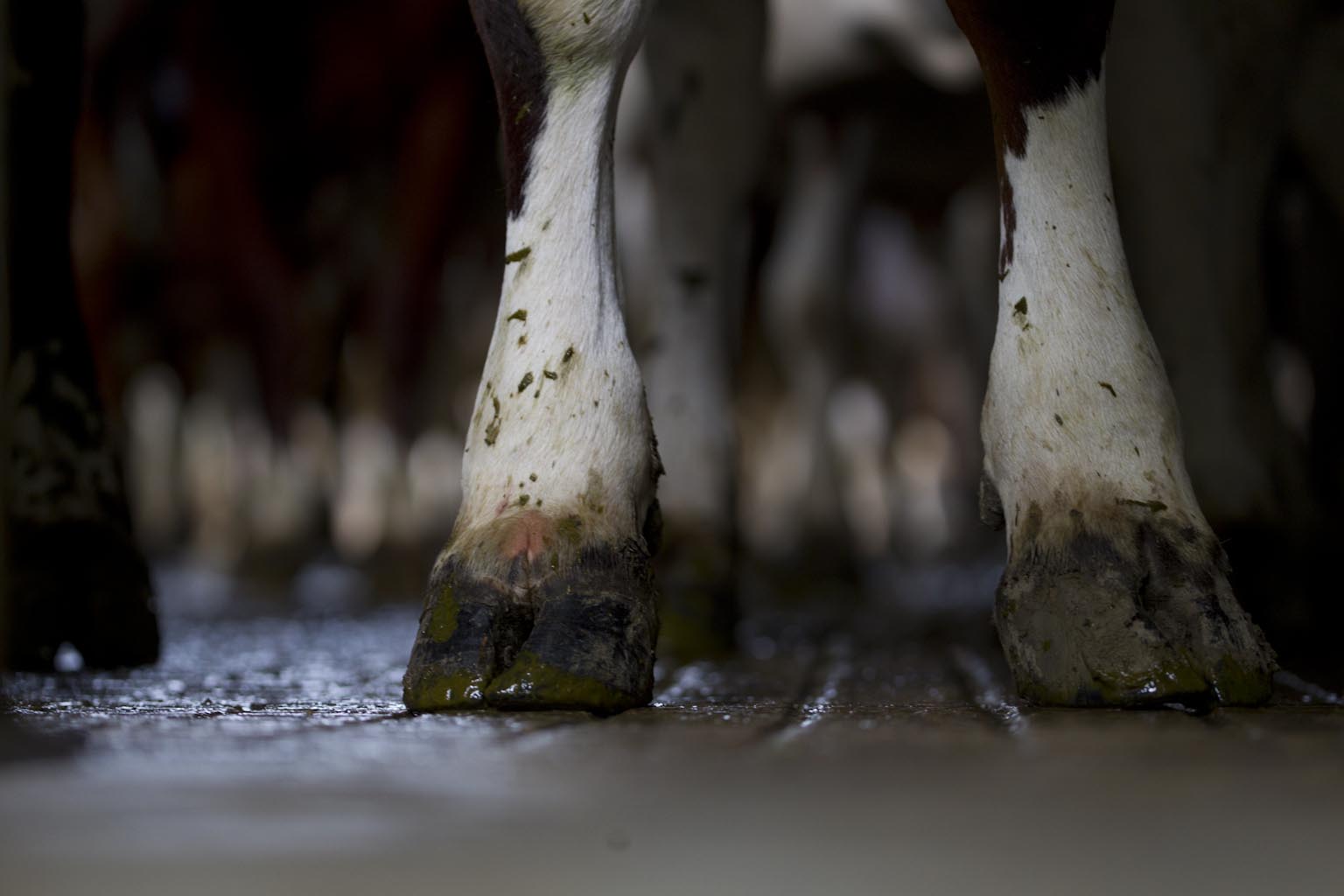
- Digital dermaitis (DD) treponemes were identified in the bovine gastro-intestinal (GI) tract, primarily the gingiva and recto-anal junction (RAJ)
- DD treponemes do not appear to cause damage to the host in the GI tract.
- DD treponemes were able to be cultured/isolated from faeces demonstrating evidence for faecal shedding as one route of transmission.
- DD treponemes have the ability to survive in sterile faeces for a median of 1 day and a maximum of 6 days which would enable transmission of viable bacteria to another animal’s foot.
- Given involvement with the GI tract and faeces, increasing hygiene on farm should help to reduce DD on farm.
When considering infection reservoirs other than the host:
- Fomites:
- The DD treponemes were detected in dairy cattle fomites (surfaces touched by affected feet/lesions)
- including hoof trimming knives, trimming equipment, gloves and in footprints
- Fomites should be considered important infection reservoirs.
- Improving biosecurity and foot trimming practices should help reduce disease spread.
- The DD treponemes were detected in dairy cattle fomites (surfaces touched by affected feet/lesions)
- Bedding:
- DD bacteria were not viable in straw or sand containing 5%(w/w) lime in the laboratory
- DD bacteria can remain viable in recycled manure solids (RMS) for 5 days, sawdust of 6 days and sand for at least 7 days
- To reduce to the risk of DD transmission the preferable bedding is straw/sand containing 5% lime
For more information the report is available.
Sector:
Dairy
Project code:
41110015
Date:
01 March 2012 - 01 September 2017
Funders:
AHDB Dairy
AHDB sector cost:
£97,802.00
Total project value:
£97,802.00
Project leader:
University of Liverpool
Downloads
41110015 final report 2018About this project
Aims and Objectives:
- To identify and characterise specific associations between bovine digital dermatitis (BDD) treponeme transmission, the bovine host and the dairy environment.
- Specific objectives:
- Development of enhanced DNA extraction techniques to aid detection of BDD treponemes
- Survey of cow and dairy farm samples for BDD treponemes using PCR, treponeme isolation and immunohistochemistry
- Understanding the ability of BDD treponemes to survive and grow in the dairy environment and under different host conditions
- Investigate the association of BDD treponemes with healthy foot tissues